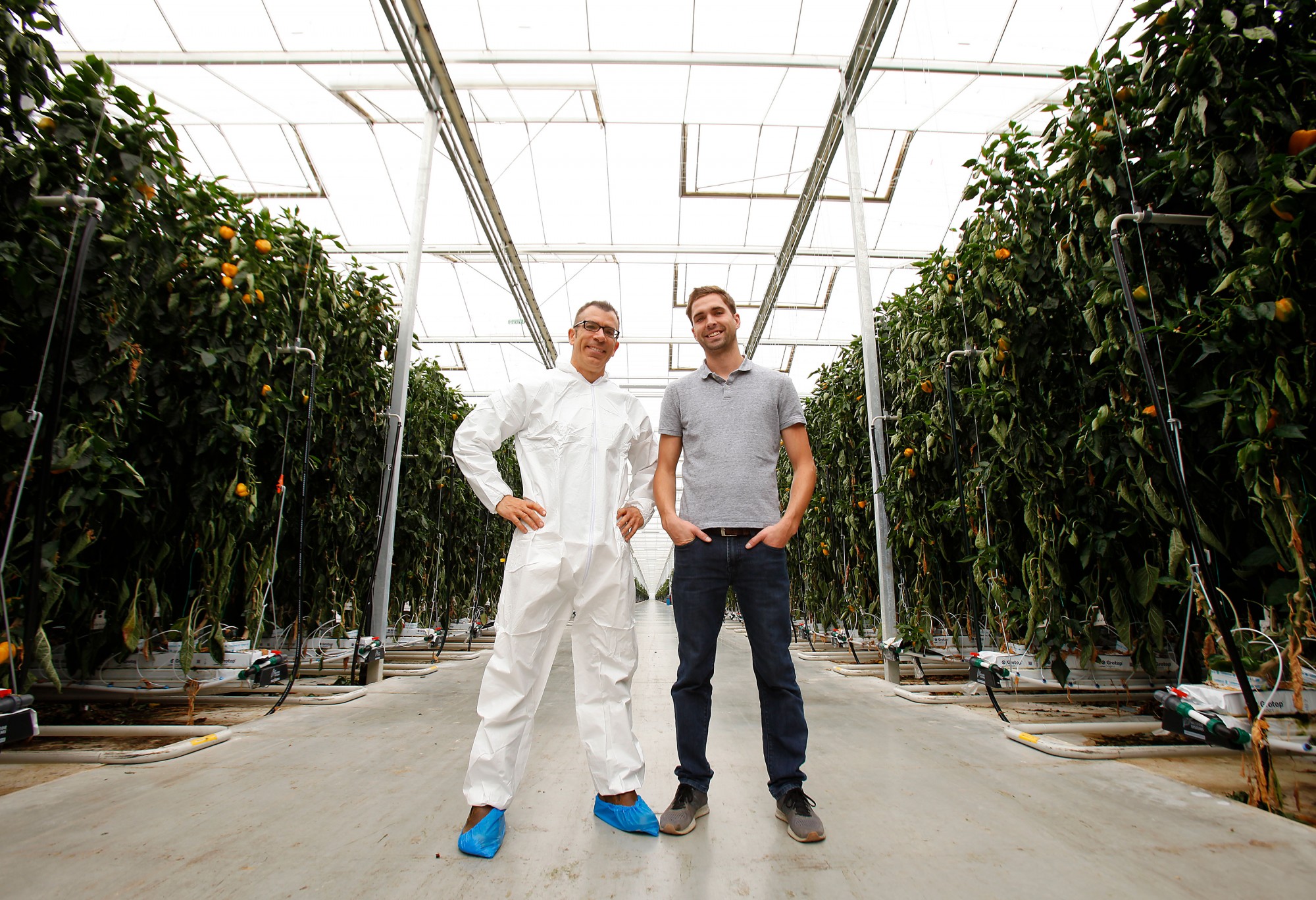
A team of University of Windsor researchers is leading a national effort on the next frontier of sustainable and accessible food.
Working with experts from government labs and industry, the multidisciplinary team is using a new growing environment modeling tool and advanced additive manufacturing — often referred to as 3D printing — to explore how leading-edge greenhouse technology can be delivered to remote locations and optimized to reduce energy costs and increase production.
“We can explore how more radical changes, like using earthen walls or solar glass, could potentially benefit a leading-edge greenhouse without ever interrupting ongoing commercial operation,” says Rupp Carriveau, the project lead and director of UWindsor’s Environmental Energy Institute.
Dr. Carriveau says the team has created energy harvesting models to design distributed, networked, power systems to provide increased and more sustainable energy for a rapidly expanding sector. Controlled environment agriculture (CEA) such as greenhouses, vertical farms, and plant factories can increase access, yield density, uniformity, and nutritional specificity of food production.